The COVID-19 pandemic has had a profound impact on alcohol consumption patterns. This led to increased usage during the crisis, a concerning trend that has continued. Here’s an overview of the relationship between high alcohol usage during and after COVID-19.
Alcohol Consumption
During the pandemic, many individuals turned to alcohol as a coping mechanism for the stress, isolation, and uncertainty.
- Alcohol consumption surged, with reports showing that about 29% of respondents in a U.S. study reported increased alcohol use during the pandemic, particularly among those with anxiety and depression symptoms.
- Alcohol sales increased significantly, particularly in the sales of hard liquor, reflecting a broader trend of increased drinking during lockdowns.
- Alcohol-related deaths rose dramatically, with a nearly 38% increase in death certificates listing alcohol as a contributing factor during the first two years of the pandemic.
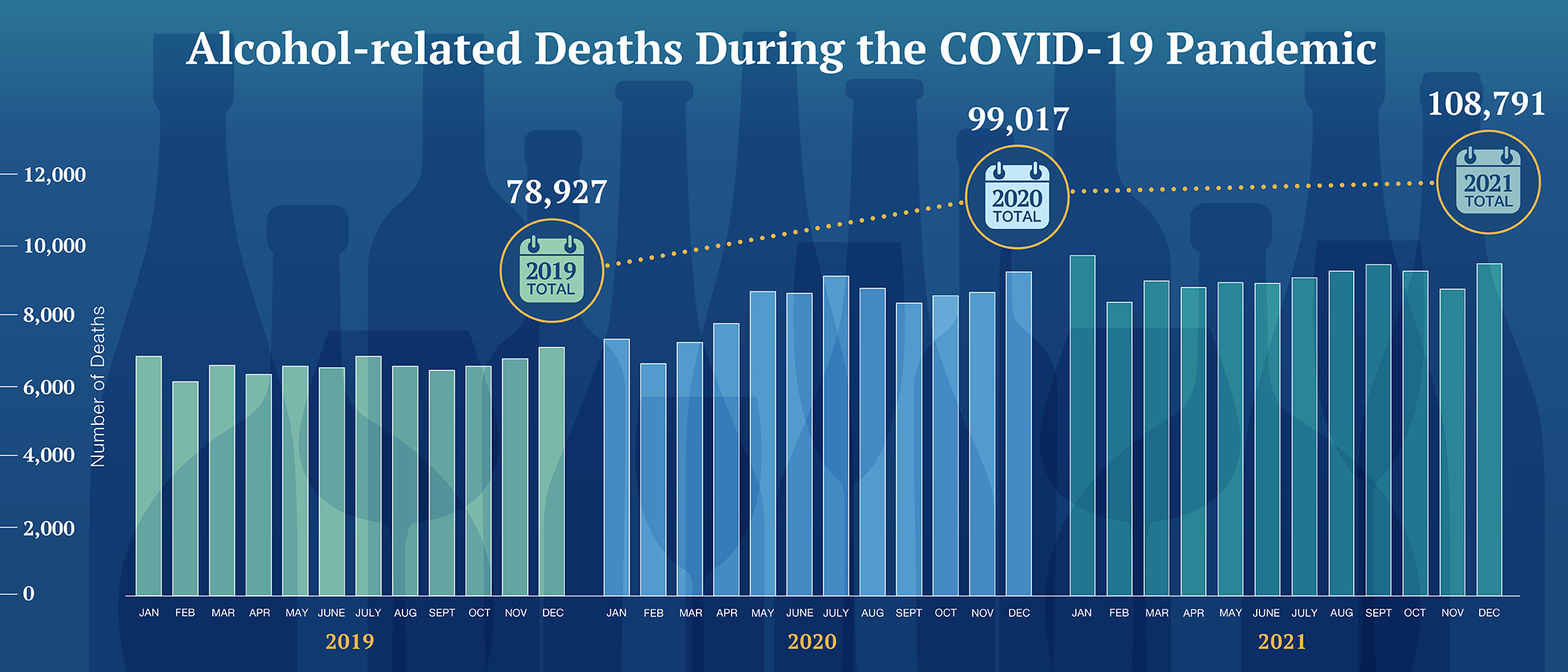
Ongoing High Alcohol Usage Post-Pandemic
Despite the easing of pandemic-related restrictions, studies show that high levels of alcohol consumption have persisted:
- A study published in the Annals of Internal Medicine found that 69.3% of Americans reported consuming alcohol in the past year in 2022, a slight increase from previous years.
- The percentage of heavy drinkers also rose to 6.3% in 2022, compared to 5.1% in 2018, indicating a troubling trend of sustained high alcohol usage.
Factors Continue High Alcohol Usage
Several factors contribute to the ongoing high levels of alcohol consumption:
- Mental Health Struggles: The pandemic exacerbated mental health issues, leading many to continue using alcohol as a coping strategy for anxiety and depression.
- Social Norms: The normalization of drinking during the pandemic has made it a common way to cope with stress, further entrenching these habits.
- Accessibility and Policy Changes: Changes in alcohol sales policies during the pandemic, such as increased availability of takeout alcohol from restaurants, may have contributed to sustained high consumption levels.
Future Considerations
The long-term consequences of increased alcohol consumption are concerning. Experts warn that continued high levels of drinking could lead to:
- Increased rates of alcohol use disorder (AUD) and related health issues among those. Who already had risky drinking behaviours before the pandemic.
- A potential rise in alcohol-related health problems, like liver disease and mental health disorders. As the effects of prolonged alcohol use become more pronounced.
The relationship between high alcohol usage during and after COVID-19 is complex and concerning. While the pandemic initially drove many to increase their alcohol consumption. This trend has not only persisted but has slightly worsened in the years following. Addressing this issue through public health interventions and increased awareness of the risks is crucial for its long-term health impacts.
Read more on Lifetips.blog














