For decades, Google has been synonymous with online search. With over 90% of global search engine market share as of 2024, it’s easy to see why the company dominates conversations about internet search. Yet, this dominance hasn’t come without scrutiny. Accusations of anti-competitive behavior, regulatory crackdowns, and rising consumer demand for privacy and innovation have placed Google in a precarious position. Now, Google appears to be taking steps to address its monopoly. But how and why would a company voluntarily loosen its iron grip on the search market?
Why Google Needs to Act
Regulatory Pressure
In recent years, governments worldwide have been tightening their antitrust scrutiny. In the United States, Google is embroiled in lawsuits alleging it used its market dominance to stifle competition, particularly by making deals with hardware manufacturers and browsers to make Google Search the default. The European Union has also slapped Google with multi-billion-euro fines for similar practices. Facing the threat of being forcibly broken up or subjected to further fines and regulations, Google has incentives to preemptively make changes to avoid harsher outcomes.
Consumer Sentiment
User expectations have evolved. Privacy-conscious users are increasingly wary of Google’s data collection practices. Competitors like DuckDuckGo have gained traction by offering a more private search experience. Google must adapt or risk losing segments of its user base to platforms that better address these concerns.
Innovation Stagnation
A lack of competition can lead to complacency. While Google has maintained its lead through innovations like AI-driven search, including Google Bard, the risk of being outflanked by more agile competitors is real. Addressing monopoly concerns could spur a renewed focus on innovation, ensuring Google’s relevance in an ever-changing tech landscape.
How Google Is Tackling the Issue
Opening the Playing Field
Google has announced initiatives to provide more visibility to competitors within its ecosystem. For example, the company’s Android operating system now includes a “choice screen” in Europe, allowing users to select their preferred search engine during device setup. Similarly, Google has committed to providing advertisers with tools to use other search engines more effectively.
Emphasizing Privacy
Google has been introducing privacy-focused features, such as search history controls, incognito modes, and commitments to limit third-party cookie tracking. While these measures aim to reassure users, they also address criticism that Google’s data dominance gives it an unfair advantage over competitors.
Investment in Alternatives
Interestingly, Google is also funding research and development in areas tangential to search. By diversifying its portfolio, the company can reduce reliance on its search business, potentially lessening the pressure to maintain absolute dominance.
Competitors in the Search Market
While Google remains the undisputed leader, other search engines are carving out niches:
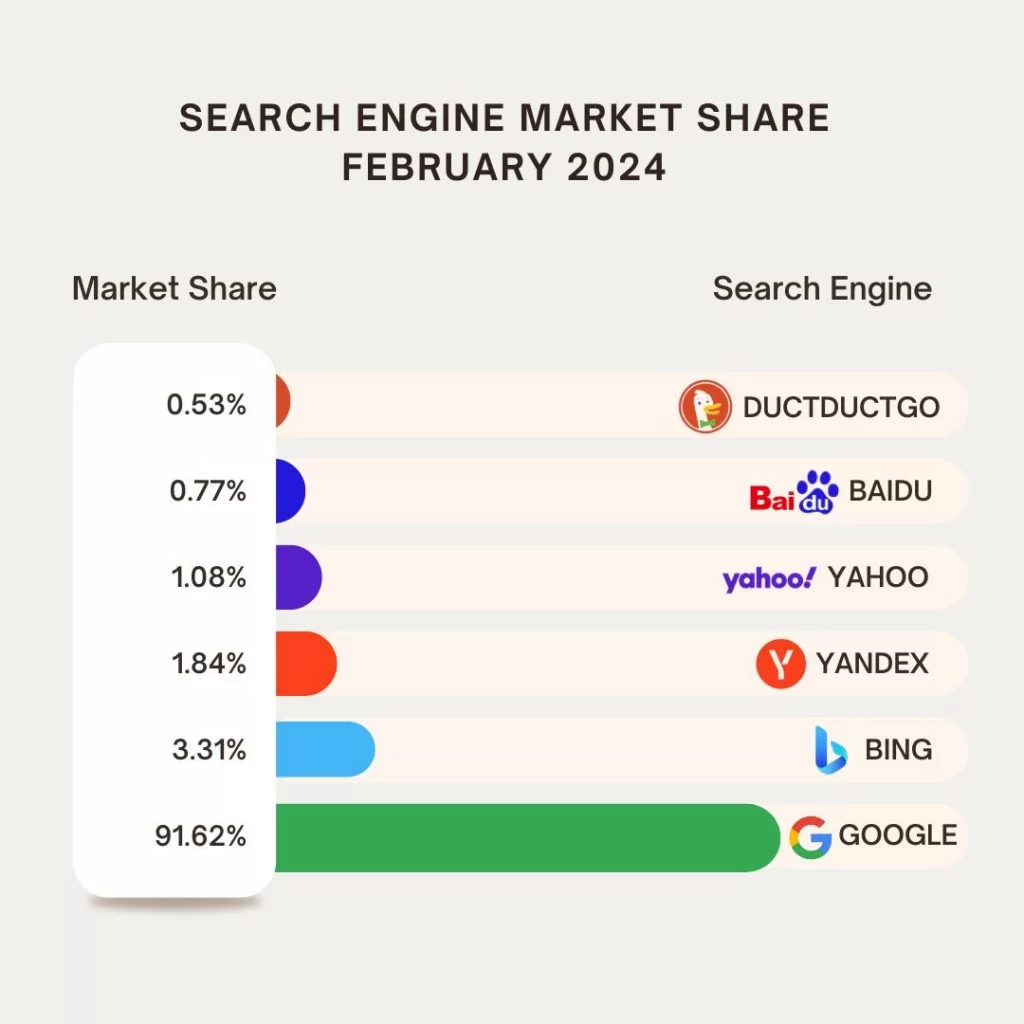
Bing (Microsoft)
Bing holds the second-largest market share globally, albeit a distant one at around 3%. With integrations into Windows and Microsoft’s AI-driven advancements through OpenAI’s GPT technology, Bing is increasingly seen as a credible alternative.
DuckDuckGo
Known for its privacy-first approach, DuckDuckGo has gained popularity among users who value anonymity. While its market share is under 1%, its growth is indicative of rising demand for alternatives that don’t monetize user data.
Baidu and Yandex
In China and Russia, Baidu and Yandex dominate their respective markets. These search engines cater to local languages and cultural nuances, filling a gap Google hasn’t been able to fully bridge due to regulatory and operational challenges in those regions.
Brave Search and Neeva
Emerging players like Brave Search and Neeva aim to disrupt the market with user-centric models. Brave leverages blockchain technology to reward users for their attention, while Neeva offers a subscription-based service with zero ads and greater control over search results.
The Future of Search
The search engine market is at a crossroads. While Google is making strides to address its monopoly concerns, the pressure from regulators, competitors, and consumers ensures the battle is far from over. Diversification and innovation will be critical for Google to maintain its position without inviting further scrutiny. Meanwhile, smaller players are seizing the opportunity to redefine what search can be in an era of privacy, personalization, and AI.
By addressing its dominance head-on, Google isn’t just fixing its monopoly; it’s shaping the future of search. Whether this future includes a more balanced ecosystem or a new kind of market leader remains to be seen. But one thing is certain: competition, when allowed to thrive, benefits everyone.














