China’s space exploration program has achieved remarkable milestones in recent years, underscoring its growing prowess in space technology and exploration. From ambitious lunar missions to innovative commercial ventures, China’s advancements are reshaping the global space landscape.
Lunar Exploration: Chang’e Missions
China’s Chang’e lunar program has made significant strides. In May 2024, the Chang’e-6 mission successfully landed on the Moon’s far side, collecting unique lunar samples. This mission marked a historic first, as no other country has retrieved samples from this region. The Chang’e-6 mission is part of China’s broader strategy to establish a lunar base near the Moon’s south pole by 2035, aiming to utilize lunar resources and conduct scientific research.
Mars Exploration: Tianwen Missions
China’s Mars exploration efforts have been equally impressive. The Tianwen-1 mission, launched in July 2020, successfully landed the Zhurong rover on Mars in May 2021. This achievement made China the second nation to land and operate a rover on Mars, following the United States. Building on this success, China has unveiled plans for crewed Mars missions, with the first anticipated in 2033. These missions aim to establish a permanent human presence on Mars, reflecting China’s long-term commitment to interplanetary exploration.
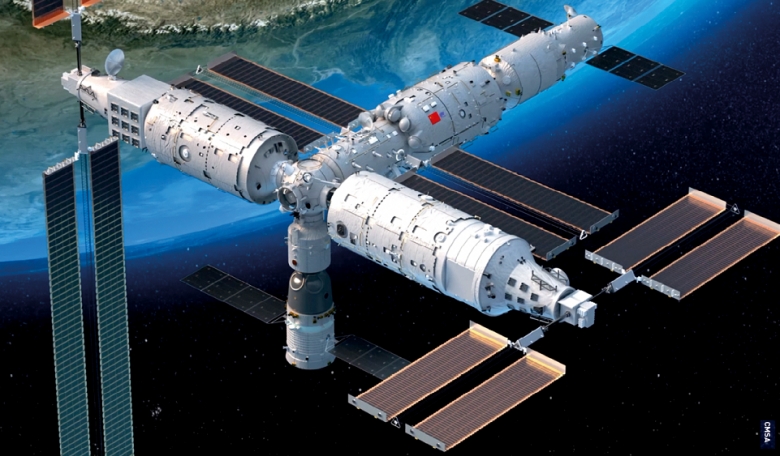
Space Station: Tiangong Program
China’s Tiangong space station represents a significant leap in its human spaceflight capabilities. The station, which became operational in 2022, serves as a microgravity laboratory for scientific research and international collaboration. In November 2024, a new crew of astronauts successfully docked with Tiangong, conducting experiments and maintaining the station’s systems. This mission underscores China’s growing influence in space exploration and its ability to sustain long-term human presence in orbit.
Commercial Space Innovations
China’s commercial space sector is experiencing rapid growth, driven by technological innovations and increased investment. Reusable rocket technology has become a focal point, with companies like Space Pioneer, CAS Space, Galactic Energy, and LandSpace conducting extensive test flights. These efforts aim to achieve first-stage recovery and reuse, potentially reducing the cost of space access and enabling more frequent launches.

Additionally, China has unveiled the Cuantianhou spaceplane, designed for high-speed suborbital flights. This reusable craft aims to offer flexible, on-demand transportation for satellites, cargo, and even passengers, marking a significant advancement in commercial spaceflight capabilities.
International Collaborations and Strategic Alliances
China is actively expanding its space collaborations globally. In Africa, China has established 23 bilateral space partnerships, providing satellites, ground stations, and other space technologies. This initiative aligns with China’s Belt and Road Initiative and reflects its ambition to enhance its global surveillance network and become a leading space power.
Future Prospects
Looking ahead, China has outlined ambitious plans for space exploration. The Tianwen-2 mission, scheduled for launch in 2025, aims to sample near-Earth asteroids and probe main-belt comets. Additionally, the Tianwen-3 mission plans to return samples from Mars, further demonstrating China’s commitment to deep space exploration.
In summary, China’s recent innovations in space exploration highlight its rapid advancement and strategic vision. Through a combination of ambitious missions, technological innovations, and international collaborations, China is solidifying its position as a formidable player in the global space arena.














