Recent advancements in the pharmaceutical industry have significantly influenced how we approach early-stage Alzheimer’s treatment. The new Alzheimer’s drugs. What do they do?. Among these breakthroughs are donanemab and lecanemab, both emerging as promising options for patients grappling with this debilitating condition.
Unpacking Donanemab – A Closer Look at Kisunla
Donanemab is the brand name Kisunla in the UK. It has gained significant attention after receiving approval from the Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA). This is a treatment for individuals with early-stage Alzheimer’s disease. This drug is a disease-modifying therapy, which aims to alleviate symptoms tackle and the root causes of Alzheimer’s disease.
What Makes Donanemab Unique?
Donanemab functions developed by Eli Lilly and interacts with amyloid proteins present in the brain. Recognizing and eliminating these harmful proteins, donanemab seeks to slow the progression of cognitive decline.
The mechanism behind donanemab operates within the framework of the body’s immune response. Translating this concept to Alzheimer’s, a pioneering approach could fundamentally change the landscape.
Clinical Trials and Their Implications
Clinical testing serves as the backbone of any new drug’s viability, and donanemab’s trials reveal promising outcomes. In the TRAILBLAZER ALZ2 trial, results indicated that those who received donanemab experienced a noteworthy 20% reduction in memory and cognitive decline. Moreover, participants entering the trial with fewer Alzheimer’s symptoms benefitted even more, showcasing the potential advantages of early intervention.
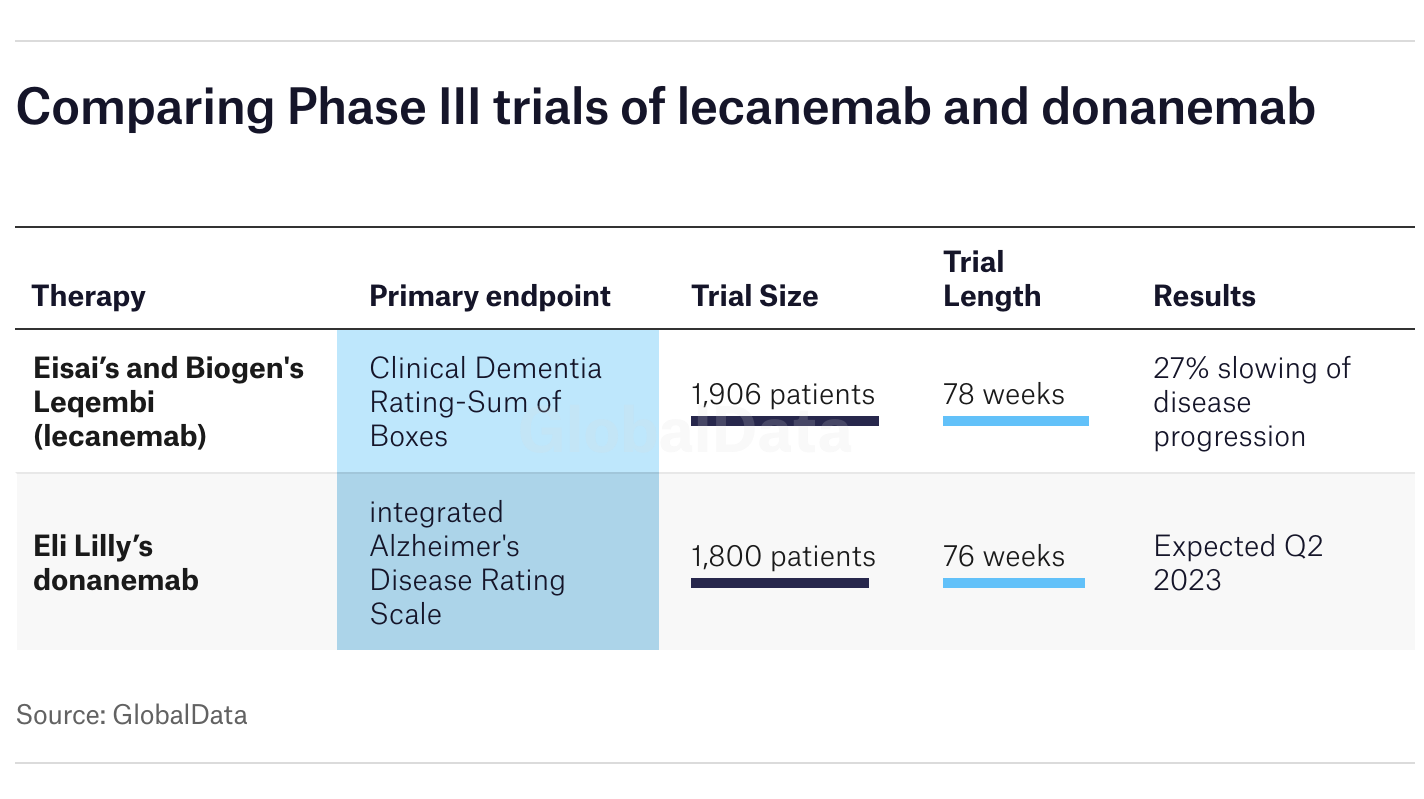
Research findings underscore an important caveat: while immediate results appear positive, the long-term impacts of donanemab remain uncertain. Given that the trial spanned only 18 months, further investigation is required to ascertain the sustainability of cognitive improvements post-treatment. It raises critical questions about the trajectory of Alzheimer’s care moving forward—how will ongoing monitoring and assessment shape our understanding of these drugs?
Addressing Patient Concerns and Side Effects
As with any novel treatment, discussions surrounding safety and side effects are paramount. Clinical trials for donanemab reported instances of headaches, infusion reactions, and neurological changes linked to amyloid clearance. Although the majority of these side effects were mild or asymptomatic, a small percentage of participants did experience serious complications, including fatalities related to treatment.

Conversations surrounding the risks associated with donanemab should inform potential patients and their families as they navigate treatment decisions. Transparency regarding side effects is crucial for fostering informed consent, especially when considering the delicate balance between potential benefits and adverse reactions. Ultimately, patient education plays a foundational role in empowering individuals to make choices that align with their health priorities.
Lecanemab – Another Player in the Field
Lecanemab, marketed as Leqembi, stands alongside donanemab as another frontrunner in the race for effective early-stage Alzheimer’s treatments. Both drugs share similar goals, namely modifying the disease process instead of merely managing its symptoms. However, as with donanemab, it faces scrutiny from various regulatory bodies, particularly the National Institute of Health and Care Excellence (NICE), which recently opted against recommending lecanemab for NHS provision.
Mechanism of Action
Like donanemab, lecanemab targets beta-amyloid plaques—the abnormal clumps of protein that accumulate in the brains of Alzheimer’s patients. By binding to these plaques, lecanemab enhances their clearance via the immune system. The underlying theory posits that reducing the amyloid burden may alleviate the neurologic impact of Alzheimer’s disease, potentially preserving cognitive function.
This duality of targeting the root cause while minimizing symptomatic expression makes both drugs noteworthy contenders. However, the complexities involved in their administration, costs, and overall accessibility remain significant barriers that warrant discussion. Navigating the nuances of healthcare policy and drug availability requires collaborative efforts between pharmaceutical companies, regulatory agencies, and healthcare systems.
Insights into Access and Inequities
The question of access extends beyond mere affordability; it encompasses broader systemic issues that affect diverse populations across the UK. Approximately 91.5% of trial participants for donanemab were white, sparking concerns about the representativeness of study results. Diverse clinical trials are essential to ensure that therapeutic breakthroughs translate effectively across various demographics.
Efforts to include underrepresented groups in clinical research are crucial for validating the applicability of new treatments. Furthermore, regulatory frameworks must account for these disparities to maintain equitable access to groundbreaking therapies. How can healthcare systems adapt to ensure that all individuals, regardless of socio-economic background or ethnicity, benefit from advancements in Alzheimer’s treatment?
Cost-Effectiveness and Healthcare Policy Considerations
When evaluating the landscape of new Alzheimer’s drugs, considerations around cost and healthcare policy loom large. The rejection of donanemab and lecanemab by NICE signals the need for a rigorous examination of how these treatments fit into existing healthcare frameworks.
Financial Implications of New Treatments
Both donanemab and lecanemab come with substantial price tags, raising questions about the sustainable incorporation of such drugs within public healthcare systems. With the potential for significant upfront costs, stakeholders must grapple with budgeting for innovations that may provide long-term benefits but require considerable initial investment.
Healthcare economics plays a pivotal role in determining which treatments receive funding and prioritization. Policymakers face the daunting task of balancing budgetary constraints against the pressing needs of populations affected by degenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s. Crafting policies that prioritize effective treatments while accounting for financial realities will be essential for equitable healthcare delivery.
Reimagining the Future of Alzheimer’s Treatment
The evolving landscape of Alzheimer’s treatment calls for innovative thinking and a proactive stance. If healthcare systems continue to embrace new therapies, there must also be a commitment to addressing systemic inequities, optimizing access, and cultivating an environment where every individual can benefit from advances in medicine.

By reimagining care models that incorporate cutting-edge treatments like donanemab and lecanemab while simultaneously championing inclusive practices, we can create a more equitable future for Alzheimer’s patients and their families.
Conclusion
The emergence of the new Alzheimer’s drugs marks a critical juncture in the ongoing battle against this complex disease. This shows the promise of altering the course of early-stage Alzheimer’s. It helps you get treatment, have discussions and access must remain at the forefront of healthcare discourse. As we explore the implications of these advancements, we must advocate for equitable access while emphasizing the importance of diversity in clinical trials.
The journey toward effective Alzheimer’s treatment is far from over; it demands collaboration, innovation, and a steadfast commitment to improving the lives of those impacted by this challenging condition. As researchers, policymakers, and advocates work together, we must keep the patient experience central to our efforts, ensuring that breakthroughs translate into tangible benefits for all individuals battling Alzheimer’s disease.
Read more on Lifetips.blog













