India is at a pivotal moment in its energy strategy, with renewed efforts to expand its nuclear power capacity. This initiative leads to the need for sustainable energy solutions. It aims to support the country’s ambitious economic growth targets while addressing climate change commitments.
Nuclear Energy in India
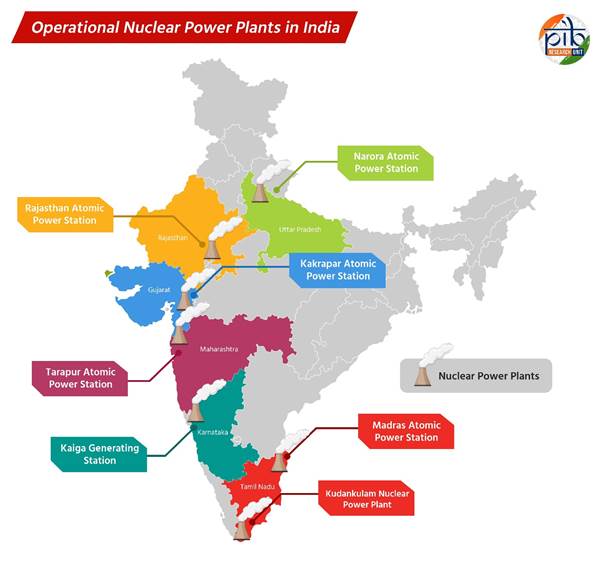
Since its independence in 1947, India has pursued a robust nuclear program by Homi Bhabha and Jawaharlal Nehru. The Atomic Energy Commission in 1948 was the beginning of India’s journey towards harnessing nuclear energy for economic development. However, despite early promises of nuclear power contributions, the actual installed capacity has lagged behind expectations. It is currently standing at approximately 7,425 megawatts. Which accounts for only about 3% of the total electricity production in the country.

Recent Developments and Future Goals
In recent years, the Indian government has set ambitious targets to revitalize its nuclear energy sector. The Finance Minister, Nirmala Sitharaman, announced plans to expand nuclear capacity to 100 gigawatts by 2047. This aligns with the broader vision of making India a developed nation by its centenary of independence. This includes the introduction of Bharat Small Reactors by 2033 and amendments to existing legislation to encourage private sector participation in nuclear energy.

Challenges Sector
Despite the optimistic outlook, India’s nuclear program faces several challenges. Historically, the country has struggled with high upfront capital costs, land acquisition issues, and public opposition to nuclear projects. Additionally, the lack of indigenous uranium and the historical isolation from international nuclear trade have necessitated a unique approach to developing a thorium-based fuel cycle. The government has acknowledged these hurdles and is working to address them through policy reforms and international collaborations.
Collaborations and Partnerships
India’s nuclear ambitions are also supported by international partnerships. Recent agreements with countries like the United States and France aim to enhance civil nuclear cooperation, facilitating technology transfer and investment in the sector. These collaborations are crucial for overcoming the technological and financial barriers that have historically hindered the growth of nuclear energy in India.
Conclusion
As India seeks to balance its energy needs with environmental responsibilities, the revival of its nuclear program represents a critical component of its energy strategy. With ambitious targets set for the coming decades and a commitment to international collaboration, India is poised to enhance its nuclear capacity, contributing to a sustainable energy future.
Read more on Lifetips.blog














