The Oder River in Poland has faced a devastating ecological disaster due to toxic algae blooms in recent years. This blog post explores the causes of the algae crisis, including high salinity levels from industrial pollution. And the efforts by local activists and authorities to save the river’s delicate ecosystem. It discusses the long-term challenges of restoring the Oder and preventing future algae outbreaks in the face of climate change.
The Oder River’s Ecological Disaster
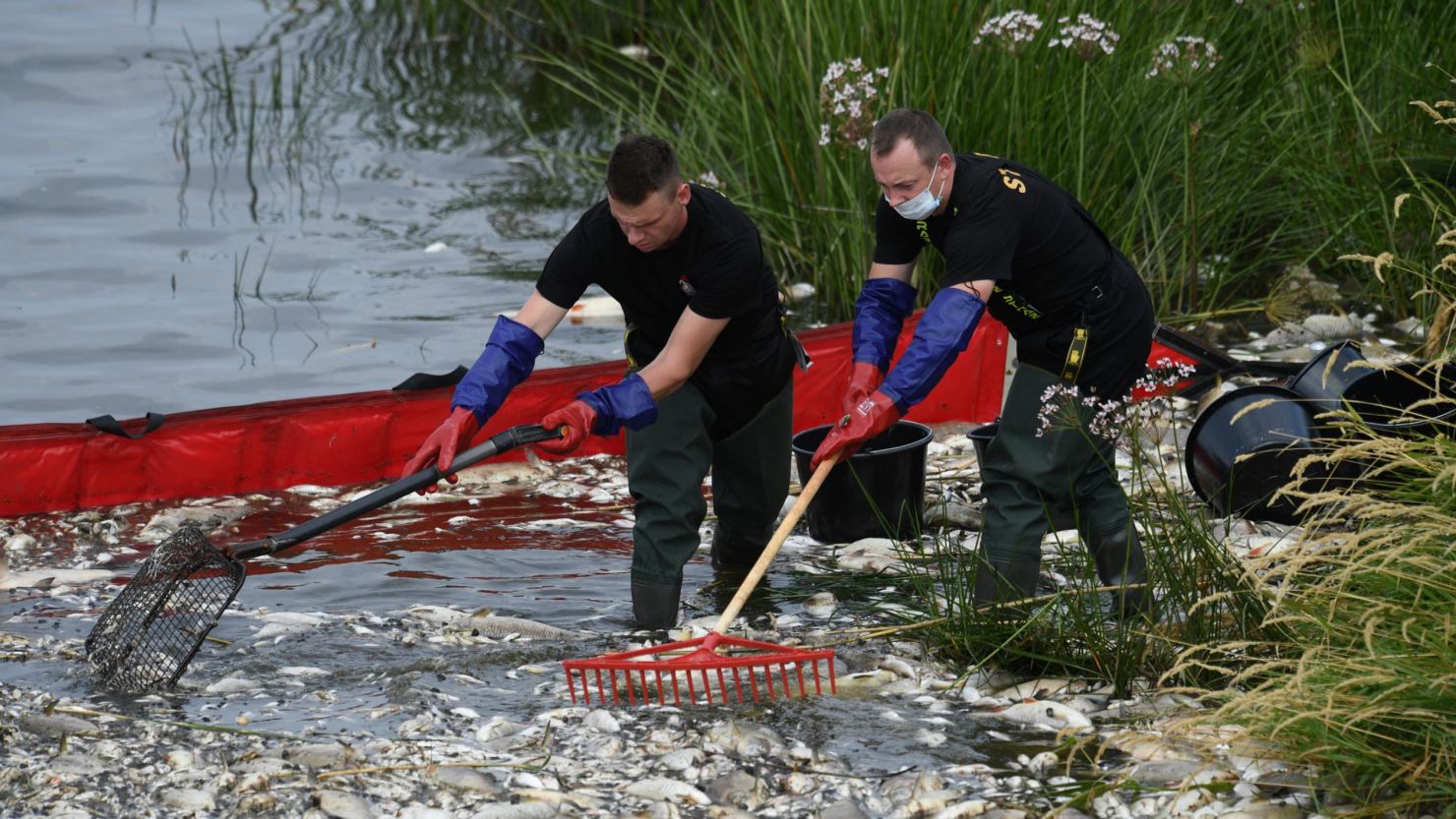
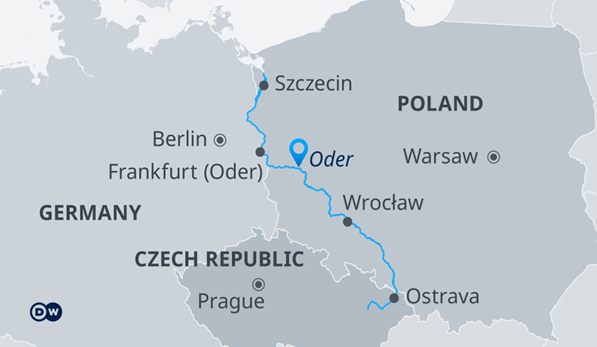
It is Poland’s second-largest river and has faced a severe environmental crisis in recent years due to toxic algae blooms. In the summer of 2022, a devastating bloom of the microalga Prymnesium parvum killed off an estimated 360 tonnes of fish in neighbouring Germany and a domestic political crisis.

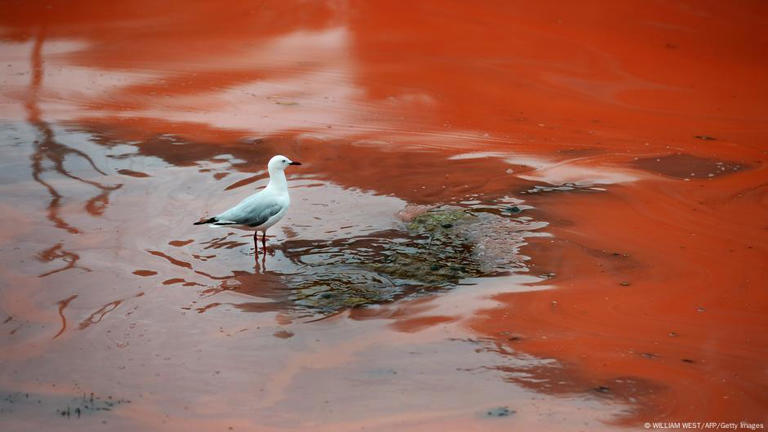
The root causes of this crisis are multifaceted. Climate change, high salinity levels, and industrial pollution have all contributed to the proliferation of these harmful algae. Waters have become increasingly saline due to the discharge of wastewater from coal mines. Other industrial activities, provide the ideal conditions for the growth of Prymnesium parvum.
Tackling the Salinity Problem
Experts agree that the key to preventing future algae blooms lies in reducing the salinity levels in the Oder River. Authorities must significantly lower the current wastewater threshold values for what coal mines and other companies are allowed to discharge into the river. This will be a crucial step in creating a less favourable environment for the toxic algae to thrive.

Reducing Nutrient Pollution
In addition to addressing the salinity issue, reducing the concentrations of plant nutrients like phosphorus and nitrogen in the Oder River is also essential. These nutrients, primarily discharged through inadequately treated wastewater and agricultural runoff, can further fuel the growth of harmful algae.

Strengthening Monitoring and Enforcement
Effective monitoring and enforcement of environmental regulations are crucial to preventing future algae crises. The 2023 EU report on the Oder disaster highlighted the need for better monitoring of industrial impacts and stronger enforcement of environmental laws at the national level.
Restoring the Oder’s Ecosystem
While immediate actions are needed to address the salinity and nutrient pollution, long-term efforts to restore the Oder’s natural ecosystem are also crucial. This may involve measures such as renaturalizing the river, improving forest management in the river basin, and supporting the recovery of the river’s biodiversity.
Overcoming Political Obstacles
The Oder River crisis has become a political battleground, with the current government coalition struggling to find a unified approach. Activists have criticized the lack of decisive action, despite pre-election promises. Overcoming these political obstacles and ensuring a coordinated, long-term strategy will be essential for the Oder’s recovery.
Conclusion
The Oder River’s algae bloom crisis is a complex challenge that requires a multifaceted approach. By addressing the root causes of high salinity and nutrient pollution, strengthening environmental monitoring and enforcement, and restoring the river’s natural ecosystem, Poland can work to prevent future ecological disasters and safeguard this vital waterway for generations to come.














